Top Insights
Critical Grandstream GXP1600 Vulnerability Allows Silent Call Interception and Remote Root Access
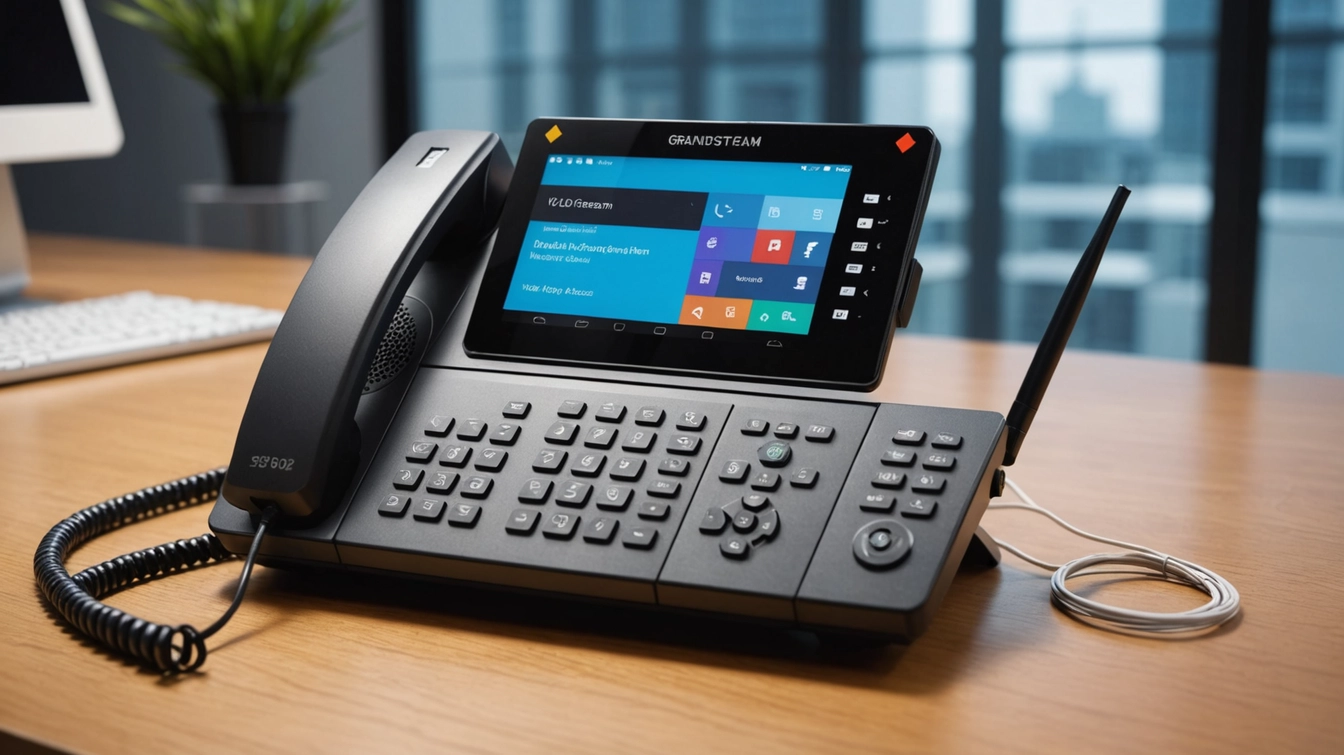

A critical vulnerability has been discovered in Grandstream’s GXP1600 series VoIP phones that could allow attackers to intercept calls and execute code remotely with root privileges. Tracked as CVE-2026-2329, the flaw is a stack-based buffer overflow that can be exploited without authentication, making it particularly dangerous for small and medium-sized businesses that commonly use these devices.
Security researchers at Rapid7 reported that an attacker exploiting this vulnerability could extract sensitive information, including local and SIP account credentials. With root access, the attacker could reconfigure the device’s SIP settings to route calls through infrastructure they control, enabling silent and transparent call interception. Users would see normal dial tones and displays, but conversations—including confidential business discussions or personal matters—could be eavesdropped on in real time.
Douglas McKee, director of vulnerability intelligence at Rapid7, noted that while exploitation requires skill and technical knowledge, the vulnerability lowers the barrier to serious attacks, especially in lightly segmented or exposed network environments. Grandstream devices have previously been targeted for botnet inclusion and other attacks, increasing concern about potential exploitation.
The vulnerability was responsibly disclosed to Grandstream in January 2026, and the company released a patched firmware version 1.0.7.81 within a week. Both Rapid7 and Grandstream have published advisories detailing the vulnerability and mitigation steps.
- call interception
- CVE-2026-2329
- enterprise VoIP risk
- Grandstream GXP1600 vulnerability
- Grandstream security advisory
- Rapid7 security report
- remote code execution
- root access vulnerability
- silent eavesdropping risk
- SIP credential theft
- small business VoIP security
- stack-based buffer overflow
- VoIP firmware patch
- VoIP phone exploit












This vulnerability highlights the risks of using exposed or lightly segmented VoIP devices in business environments. Attackers gaining root access can silently intercept calls and steal credentials without detection. It’s crucial for organizations using Grandstream phones to update to the patched firmware immediately and ensure proper network segmentation to mitigate potential exploitation.